The outputs of the Blade aerodynamical station sensor are the same as the Blade [Span] sensor , but their evolution in time is given, rather than accross the blade.
Blade aerodynamical station sensor
A blade is divided into a number of
Blade aerodynamical station
, where aerodynamic properties are evaluated. The number of blade aerodynamical stations and their locations is defined in the
Blade shape file
.
The
Blade aerodynamical station
sensor enables to track how the different output at the
Blade aerodynamical station
evolve in time. It can be opened by right-clicking on a blade aerodynamical station and toggling the sensor on, as shown in the following picture:
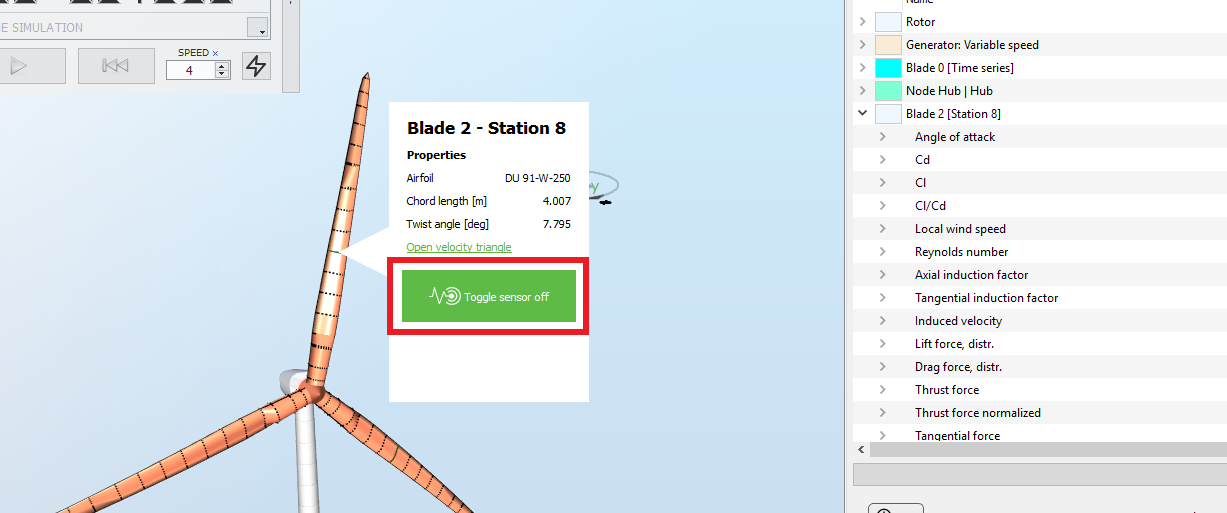
The
Blade aerodynamical station
sensor has the following fields, computed with the
BEM algorithm
:
| Field | Unit | Description |
| Angle of attack | deg | The angle bewteen the relative wind and the chordline |
| Cd | - | Drag coefficient |
| Cl | - | Lift coefficient |
| Cm | - | Moment coefficient |
| Cl/Cd | - | Ratio of lift over drag coefficients |
| Local wind speed | m.s -1 | Wind speed at the station in the horizontal plane. Note that this is only the magnitude of the wind at the blade aerodynamical stations: it does not include the effects of tilt, yaw, cone angles or the deflections of the blade |
| Relative velocity | m.s -1 | Magnitude of the sum of the wind velocity, rotational velocity and induced velocity |
| Reynolds number | - | Reynolds number at the station, calculated with the chordlength, the relative velocity and the kinematic viscosity as defined in the Environment part |
| Mach number | - | Mach number at the station, calculated as the ratio between the Relative velocity and the speed of sounds (tajen as 343 m.s -1 ) |
| Axial induction factor | - | as calculated with the BEM method |
| Tangential induction factor | - | as calculated with the BEM method |
| Axial Induced velocity | - | Induced velocity in the direction of the incoming wind, as calculated with the BEM method |
| Tangential Induced velocity | - | Induced velocity in the rotational direction of the blade aerodynamical station, as calculated with the BEM method |
| Lift force, distributed | N.m -1 | Aerodynamic force in the direction perpendicular to the incoming wind |
| Drag force, distributed | N.m -1 | Aerodynamic force in the direction of the incoming wind |
| Thrust force | N.m -1 | Aerodynamic force in the main shaft direction divided by the element length (see Section 4 in Steady BEM ) |
| Torque force | N.m -1 | Aerodynamic force in the direction of rotation of the blade aerodynamical station (see Section 4 in Steady BEM ) |
| Deflection (out-of-plane) | m | Out-of-plane displacement of the blade aerodynamical station. |
| Deflection (in-plane) | m | In-plane isplacement of the blade aerodynamical station. |
| Moment (magnitude) | Nm | Magnitude of the bending moment |