Earthquake Opensees
This benchmark verifies Ashes' earthquake simulation capabilities against
OpenSees 3.7.1
, an open-source finite element software widely used for earthquake engineering simulations. The test compares the dynamic response of a cantilever beam structure subjected to various ground motion scenarios.
1 Test Description
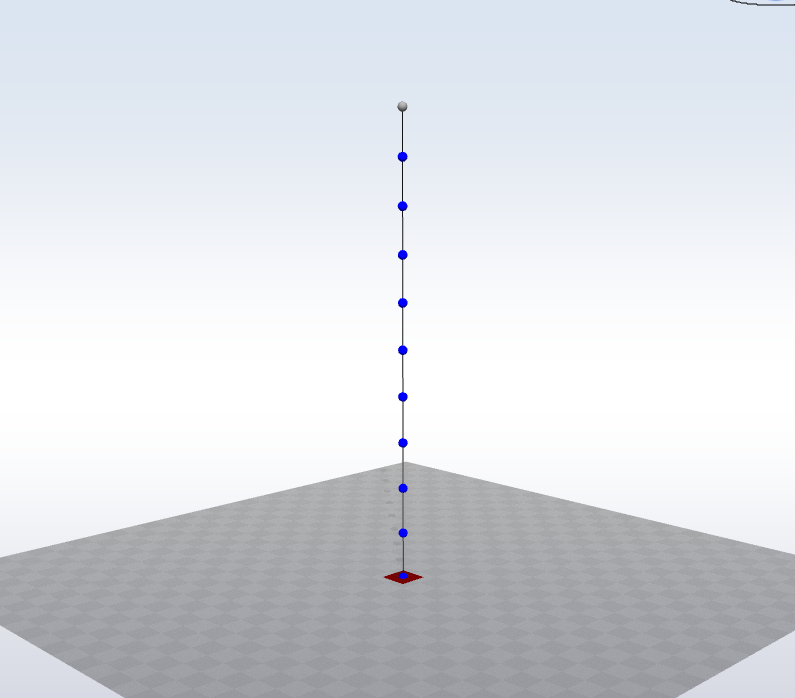
The test model consists of a cantilever beam representing a simplified wind turbine tower structure. The beam is fixed at the base and free at the top, where a concentrated mass is applied.
1.1 Model Geometry and Properties
The cantilever beam has the following characteristics:
- Height: 100 m
- Cross-section: Uniform circular hollow section
- Outer diameter: 4 m
- Wall thickness: 30 mm
- Top mass: 150 t
- Discretization: 10 beam elements of equal length
1.2 Simulation Settings
The simulation is configured with the following parameters:
- Analysis type: Linear dynamic analysis
- Damping: Stiffness-proportional damping with 5% damping ratio on the first mode (4.39 s)
- Duration: 70 seconds
- Solver: Time-domain integration
1.3 Load Cases
Five different ground motion scenarios are simulated to verify the earthquake response across various loading conditions:
- Constant acceleration in X direction: Uniform ground acceleration of 1 m/s2 applied in the global X direction
- Constant acceleration in Y direction: Uniform ground acceleration of 0.5 m/s2 applied in the global Y direction
- Sinusoidal acceleration in X direction: Harmonic ground motion of amplitude 10 m/s2 and period 3 s in the X direction
- Sinusoidal acceleration in Y direction: Harmonic ground motion of amplitude 5 m/s2 and period 1 s in the Y direction
- Northridge earthquake: Real earthquake record with acceleration time histories in X, Y, and Z directions
2 Comparison Methodology
The verification compares the dynamic response between Ashes and OpenSees at two critical locations:
2.1 Top Node Kinematics
At the top node of the cantilever beam, the following quantities are compared in all three global directions (X, Y, Z):
- Displacement time histories
- Velocity time histories
- Acceleration time histories
2.2 Bottom Node Internal Loads
At the base of the cantilever beam, the internal loads are compared for all six degrees of freedom:
- Axial force (Fz)
- Shear forces (Fx, Fy)
- Torsional moment (Mz)
- Bending moments (Mx, My)
3 Acceptance Criteria
The benchmark test is considered passed if the relative difference between Ashes and OpenSees results is within 0.5% for all compared quantities. The relative error is calculated as:
$$\text{Relative Error} = \frac{|\text{Ashes} - \text{OpenSees}|}{|\text{OpenSees}|} \times 100\%$$
This criterion ensures that Ashes accurately reproduces the earthquake response predicted by OpenSees, verifying the implementation of:
- Ground motion input and application
- Dynamic time integration schemes
- Stiffness-proportional damping formulation
- Structural dynamics calculations for beam elements
- Multi-directional earthquake loading
4 Results
The comparison between Ashes and OpenSees can be viewed on this link:
https://www.simis.io/downloads/open/benchmarks/current/Earthquake Opensees.pdf
https://www.simis.io/downloads/open/benchmarks/current/Earthquake Opensees.pdf
This benchmark provides confidence in using Ashes for earthquake analysis of wind turbine structures, where seismic loads may be a critical design consideration in certain geographical regions.